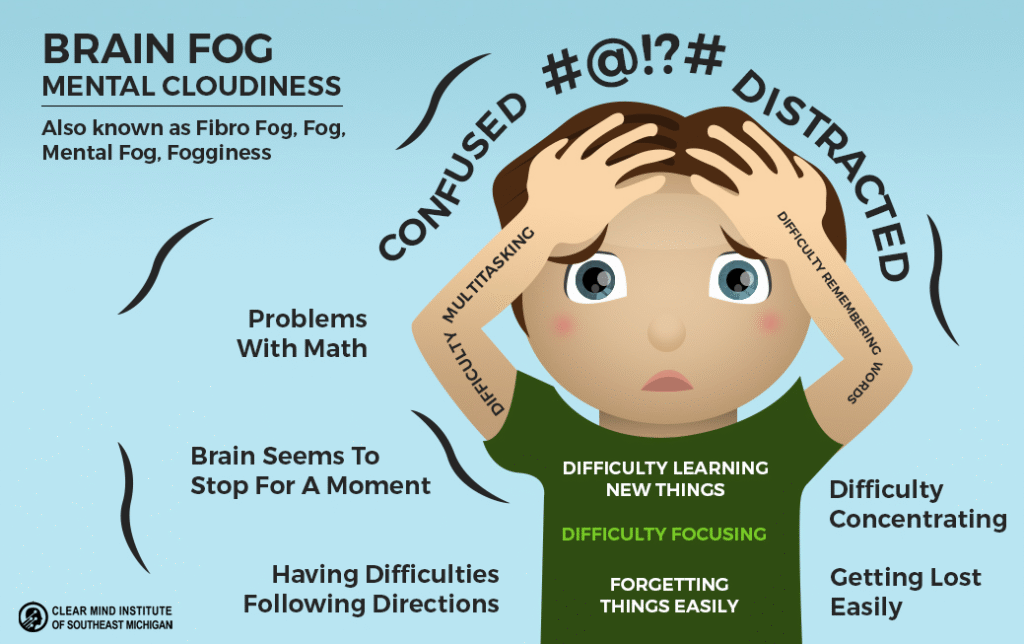
Brain fog refers to temporary cognitive dysfunction marked by forgetfulness, confusion, and poor focus. Though not a disease, it arises from issues like sleep deprivation, stress, hormonal imbalance, or nutritional deficiencies, impairing mental clarity and daily performance.
Key Takeaways
- Brain fog causes slowed thinking, memory lapses, and difficulty concentrating.
- Common triggers include poor sleep, chronic stress, and hormonal fluctuations.
- Deficiencies in vitamins (B12, D) and dehydration frequently contribute.
- Medical issues like thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, or long COVID can worsen symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes adequate rest, exercise, hydration, and balanced diet help reverse brain fog.
- Persistent or worsening symptoms require medical evaluation to rule out underlying neurological or metabolic disorders.
What Is Brain Fog?
Brain fog is not a formal medical diagnosis, but rather a group of symptoms that involve cognitive dysfunction and feelings of mental cloudiness. It is sometimes called clouding of consciousness or mental fatigue. While it does not permanently harm brain cells or intelligence, it can disrupt daily life and work by making it difficult to think, remember, and concentrate.
How Brain Fog Feels
Individuals often describe brain fog as a mental state where “everything takes more effort to process,” accompanied by a heaviness or cloud-like sensation in the mind. It leads to making mistakes, forgetfulness, mixed-up thoughts, and a need for rest even after minor cognitive tasks.
Common Signs of Brain Fog
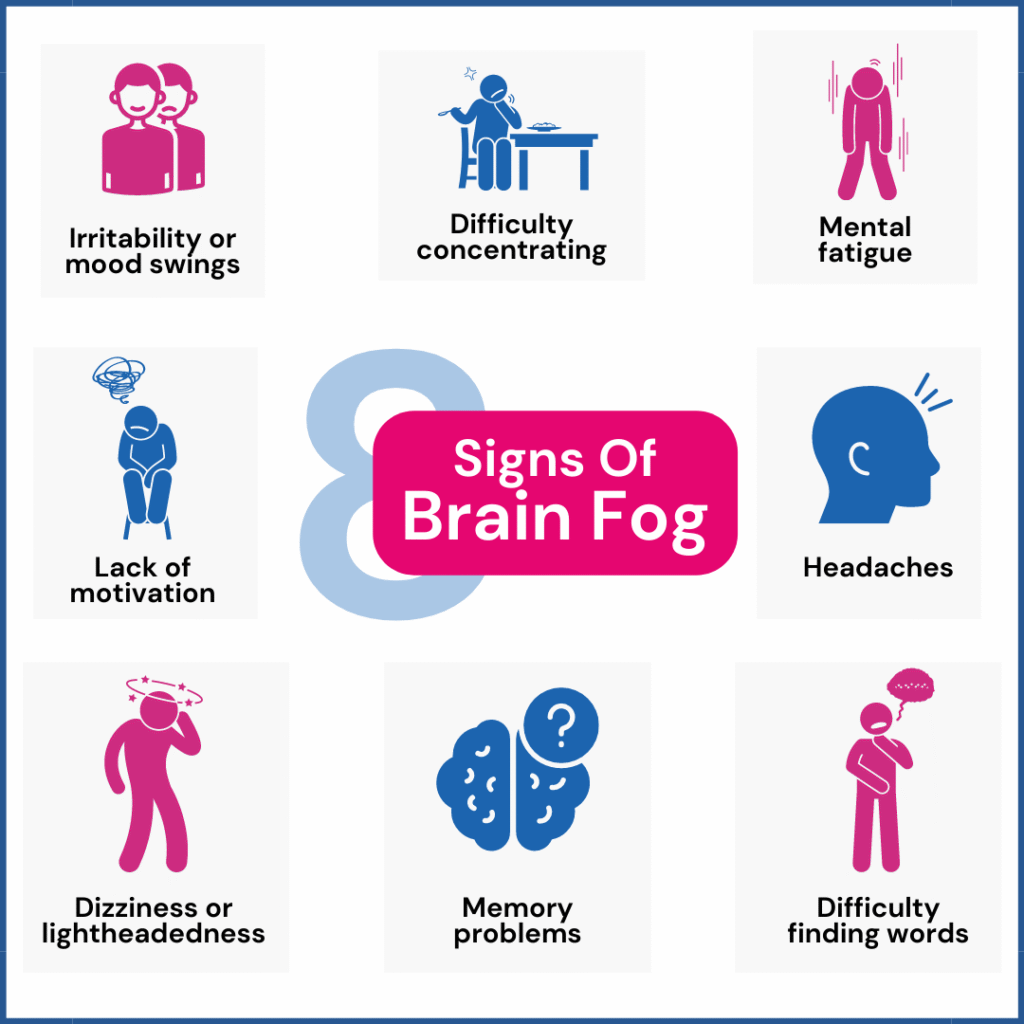
Brain fog is a common experience characterized by a range of cognitive difficulties that affect daily functioning and mental clarity. Those experiencing brain fog often report symptoms such as trouble concentrating, forgetfulness, confusion, mental fatigue, and slowed thinking. These symptoms can make even simple tasks feel overwhelming and lead to frustration, reduced motivation, and changes in mood. Understanding the detailed manifestations of these symptoms is important for recognizing brain fog and addressing any underlying causes.
- Difficulty concentrating or focusing on tasks
People may find it hard to pay attention, follow instructions, or complete activities without being easily distracted. Even familiar tasks can seem overwhelming, and sustained mental effort feels exhausting.
- Forgetfulness (such as names, dates, or why you entered a room)
Short-term memory lapses are common. You might frequently forget why you walked into a room, misplace keys, struggle to recall appointments, or blank out the names of colleagues and friends.
- Confusion or losing your train of thought
You might start a sentence or a task and then forget what you intended to say or do. Thoughts get jumbled, leading to frequent “mental stumbles” or feeling disoriented, especially when multi-tasking or under stress.
- Mental fatigue or a feeling of heaviness in the mind
The brain feels “tired” even without much mental exertion. This fatigue can make thinking and processing information seem difficult, as if your mind is “sluggish” or “in a fog.”
- Slow thinking or reaction time
Responses become delayed; you may need extra time to understand questions, make decisions, or react to changes. Tasks that usually feel automatic require more conscious effort.
- Trouble finding the right words or forming sentences
Speaking becomes more difficult as you search for words or struggle to express thoughts clearly. This can lead to awkward pauses, misspeaking, or incomplete sentences.
- Memory problems or impaired recall
There’s a noticeable decline in the ability to remember events, details, or instructions both short-term (recent conversations) and long-term memories may be affected, making it hard to retain new information.
- Difficulty multitasking
Managing several activities or thoughts at once is particularly challenging. Switching attention between tasks leads to errors or omissions, and tasks are often left incomplete.
- Reduced motivation and low self-esteem
When cognitive tasks feel extra challenging or mistakes accumulate, motivation drops. This can foster frustration, self-doubt, and a decline in confidence about handling routine or new responsibilities.
- Trouble with planning or problem-solving
Organizational skills decline, and making plans or breaking down complex problems becomes overwhelming. Understanding steps involved, anticipating outcomes, or sorting priorities may feel confusing.
- Mood changes, such as irritability or mild depression
Cognitive difficulties can affect emotional regulation, causing irritability, impatience, sadness, or mild depressive symptoms. These emotional changes are often a direct result of frustrations with mental performance.
Major Causes of Brain Fog
Brain fog is a complex condition with multiple potential causes, which can be broadly grouped into lifestyle factors, hormonal changes, and medical or environmental causes. Each category involves different mechanisms that contribute to the cognitive symptoms commonly described as brain fog.
1. Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development of brain fog, with everyday habits and choices such as sleep quality, stress management, nutrition, hydration, physical activity, and screen time directly influencing mental clarity and cognitive performance.
- Lack of Sleep: Sleep is critical for brain function, particularly attention, memory consolidation, and cognitive processing. Insufficient or poor-quality sleep impairs these functions, leading to difficulty focusing, slower thinking, and memory lapses.
- Stress: Chronic stress elevates cortisol and other stress hormones, which can cause inflammation in the brain and mental exhaustion. This reduces cognitive sharpness and motivation.
- Dietary Deficiencies: Inadequate levels of essential vitamins such as B12 can impair nerve health and cognitive function. Food allergies or sensitivities may trigger inflammatory responses that also affect brain clarity.
- Dehydration: The brain is highly sensitive to fluid balance. Even mild dehydration can reduce attention and short-term memory.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Exercise boosts blood flow and neurogenesis (growth of brain cells). Physical inactivity can contribute to sluggish cognitive function.
- Excessive Screen Time: Long hours of screen use may lead to mental fatigue, eye strain, and disrupted sleep patterns, all of which can worsen brain fog.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes greatly influence cognitive function, and fluctuations in hormones such as those occurring during pregnancy, menopause, or with thyroid disorders can disrupt brain chemistry and lead to pronounced episodes of brain fog and mental fatigue.
- Pregnancy and Menopause: Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone impact neurotransmitter systems involved in attention and memory, sometimes causing “pregnancy brain” or menopausal cognitive changes.
- Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism leads to reduced thyroid hormone levels that slow metabolism and brain functions, contributing to forgetfulness, slowed thinking, and difficulty concentrating.
3. Medical and Environmental Causes
Medical and environmental causes encompass a wide range of factors including chronic illnesses, medication side effects, infections, autoimmune conditions, mood disorders, and exposure to toxins that can significantly impair cognitive function and contribute to the persistent symptoms of brain fog.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, multiple sclerosis, and lupus often involve inflammation and immune dysregulation that negatively affect cognition.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including some antihistamines, antidepressants, and anti-cholinergic agents, may have side effects that diminish cognitive clarity.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections, including COVID-19, Lyme disease, and the aftermath of chemotherapy (“chemo brain”), can cause neurological symptoms that manifest as brain fog.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Inflammatory processes in autoimmune diseases can interfere with normal brain function.
- Mood Disorders: Depression and anxiety disrupt brain networks concerned with memory, attention, and learning, often causing cognitive slowing.
- Environmental Toxins and Pollution: Exposure to pollutants and toxins may induce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, affecting mental clarity.
Natural treatment of brain fog
Natural treatment of brain fog focuses on addressing lifestyle factors, improving daily habits, and using evidence based natural supplements or therapies. Here’s how each approach can help restore mental clarity and cognitive performance:
1. Optimize Lifestyle Habits
Optimizing lifestyle habits is a foundational step in combating brain fog, as daily routines related to sleep, nutrition, hydration, physical activity, and mental rest critically influence cognitive clarity and overall brain health.
- Improve Sleep Quality: Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep nightly. Go to bed and wake up at consistent times, limit screen exposure and caffeine before bedtime, and keep your bedroom quiet and dark. Quality sleep is essential for memory, focus, and overall brain function.
- Balanced Nutrition: Eat a varied diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats (such as those from fish, nuts, and avocados). Avoid excessive sugar and heavily processed foods, which can lead to energy fluctuations and worsen brain fog.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink water regularly; even mild dehydration can reduce memory and concentration. Monitor your intake, especially during hot weather or periods of increased physical activity.
- Physical Activity: Engage in moderate exercise (walking, jogging, yoga, cycling) for at least 30 minutes most days. Exercise increases blood flow to the brain and supports cognitive health.
- Mindful Breaks and Digital Hygiene: Take regular breaks during mentally demanding tasks to avoid fatigue. Reduce unnecessary screen time, especially before bed, to preserve sleep quality and reduce eye strain.
2. Stress and Mind-Body Management
Effective stress management and cultivating mind- body balance are essential strategies for alleviating brain fog, as chronic stress and unresolved emotional tension can profoundly disrupt cognitive clarity.
- Practice Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and yoga lower stress hormones, reduce mental tension, and improve focus. Short daily sessions can make a significant difference.
- Engage in Relaxation Activities: Hobbies, time in nature, and social interactions can reduce stress and provide mental rejuvenation.
3. Natural Supplements
Carefully choosing evidence-based natural supplements and herbs can provide additional support for mental clarity, especially when lifestyle adjustments alone are not sufficient.
| Supplement Type | Example / Name | Reported Cognitive Benefit | Evidence and Research Context |
| B Vitamins | B6, B9 (folate), B12 | May support cognitive function | Supplementation mainly helps those with deficiency; benefits in healthy individuals are not consistent. |
| Vitamin E | Vitamin E | May slow cognitive decline in dementia | Shown to benefit those with dementia; unclear preventive effect in healthy adults. |
| Vitamin C, Beta-carotene | Vitamin C, Beta-carotene | Antioxidant protection | Protective effect suspected; direct cognitive benefit of supplements not established. |
| Magnesium | Magnesium | May aid brain health | Higher dietary intake is linked to better brain health in women; benefit from supplementation is unclear. |
| Herbal | Ginseng | May improve aspects of cognition | Some studies suggest improvement in memory and mental arithmetic; more research needed. |
| Herbal | Ginkgo Biloba | Possible memory/cognitive speed boost | Evidence is mixed; some studies show mild benefits, others do not. |
| Fatty Acids | Omega-3 (fish oil) | Important for brain structure/function | Not conclusively proven to enhance cognition in healthy people through supplements. |
| Other | Creatine | May aid cognition under strain | Evidence mainly in conditions of sleep deprivation or high cognitive demand. |
| Other | L-theanine (with caffeine) | May improve attention/performance | Some evidence supports improvement in attention, especially when combined with caffeine. |
4. Additional Natural Strategies
In addition to lifestyle optimization and targeted supplementation, adopting broader natural strategies such as mindful dietary choices, balanced sugar intake, herbal remedies, and stress-reduction techniques can further support mental clarity and help alleviate brain fog.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Use caffeine in moderation for alertness, but avoid overuse, which can worsen anxiety and disrupt sleep. Limit alcohol, as it may contribute to mental sluggishness.
- Establish a Routine: Consistency in daily activities, meals, exercise, sleep reinforces healthy brain rhythms.
- Address Underlying Health Issues: Persistent brain fog may signal an underlying medical issue (thyroid problems, sleep disorders, mood disorders, nutritional deficiencies). Consult a healthcare professional if symptoms do not improve with lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Brain fog is a temporary condition characterized by mental cloudiness, difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, and slowed thinking. It can result from factors like poor sleep, stress, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, or medical issues. Although frustrating, brain fog is usually reversible by improving lifestyle habits such as getting quality sleep, eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, managing stress, and, when needed, using certain natural supplements. Persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out underlying conditions.
FAQs
What is brain fog?
Brain fog is a temporary state of mental cloudiness, causing difficulty in thinking, remembering, and focusing, but it is not a formal medical diagnosis.
What are common symptoms of brain fog?
Symptoms include difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, confusion, mental fatigue, slow thinking, trouble finding words, and mood changes like irritability.
What causes brain fog?
Causes range from poor sleep, chronic stress, hormonal changes, nutrient deficiencies, medication side effects, infections, autoimmune disorders, to environmental toxins.
Is brain fog a sign of dementia?
No, brain fog is generally not linked to dementia but may accompany other health issues like long COVID, stress, or vitamin deficiencies.
Can brain fog have long-term effects?
Brain fog itself rarely causes lasting brain damage, but underlying conditions, such as sleep apnea or depression, may have long-term cognitive impacts.
When should I see a doctor for brain fog?
Consult a healthcare provider if brain fog interferes with daily life, work, or safety, especially if symptoms persist or worsen.
How is brain fog treated?
Treatment focuses on identifying and managing underlying causes, improving sleep, nutrition, reducing stress, and sometimes using supplements or medical therapies.
Can lifestyle changes help reduce brain fog?
Yes, optimizing sleep, balanced diet, hydration, regular exercise, stress management, and limiting screen time can significantly improve symptoms.
Are there supplements that improve brain fog?
Some supplements like B vitamins, vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and herbal adaptogens may help, especially when correcting deficiencies.
Is brain fog common after COVID-19?
Yes, brain fog is a frequently reported symptom of long COVID, possibly due to brain inflammation and immune system effects.
Reference
- Ali SA, et al. (2018). Hormonal influences on cognitive function.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6422548/ - Brain fog. (n.d.).
https://www.sjogrens.org/files/brochures/brain_fog.pdf - Cognitive changes. (n.d.).
http://www.nationalmssociety.org/Symptoms-Diagnosis/MS-Symptoms/Cognitive-Changes - Csipo C, et al. (2021). Sleep deprivation impairs cognitive performance, alters task-associated cerebral blood flow and decreases cortical neurovascular coupling-related hemodynamic responses.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-00188-8 - Dass R, et al. (2023). Understanding the experience and impacts of brain fog in chronic pain: A scoping review.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10334862/ - Eide S, et al. (2020). Doxorubicin chemotherapy-induced “chemo-brain”: Meta-analysis.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32505665/ - Fibro fog. (n.d.).
http://www.arthritis.org/about-arthritis/types/fibromyalgia/articles/fibro-fog.php - Fitzgerald T, et al. (2015). Residual effects of sleep medications are commonly reported and associated with impaired patient-reported outcomes among insomnia patients in the United States.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4689974/ - Gava G, et al. (2019). Cognition, mood and sleep in menopausal transition: The role of menopause hormone therapy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6843314/ - Hanson JA, et al. (2021). Sleep deprivation.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547676/ - Kravitz HM, et al. (2015). Fibrofog and fibromyalgia: A narrative review and implications for clinical practice.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25583051/ - Mackay M. (2015). Lupus brain fog: A biologic perspective on cognitive impairment,
depression, and fatigue in systemic lupus erythematosus.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12026-015-8716-3 - Markun S, et al. (2021). Effects of vitamin B12 supplementation on cognitive function, depressive symptoms, and fatigue: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33809274/ - Sandler CX, et al. (2020). Chronic fatigue syndrome: progress and possibilities.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32248536/ - Yaribeygi H, et al. (2016). The impact of stress on body function: A review.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5579396/ - Zhou L, et al. (2019). Food allergy induces alteration in brain inflammatory status and cognitive impairments.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29339006/
Dr. Nathan Cole, MD, PhD, is a neurologist and cognitive health researcher with 13 years of experience in brain aging, neuroprotection, and nutritional neuroscience. He earned his MD and PhD in Neuroscience from Harvard Medical School and completed residency at Mass General Brigham. Dr. Cole focuses on cognitive enhancement through diet, lifestyle, and targeted supplementation. His recent work includes clinical trials on omega-3 and polyphenol support for memory and focus in aging adults.

