
Fat loss occurs when you burn more calories than you consume, creating a calorie deficit. Metabolism influences how efficiently your body converts food into energy. Certain foods naturally support this process by boosting metabolism, increasing fullness, and aiding fat oxidation. Effective fat-cutting foods are high in protein to preserve muscle, low in calorie density but high in fiber for satiety, and rich in compounds like antioxidants, omega-3s, and capsaicin.
Seventeen top Diet Plan For Weight Loss include leafy greens, lean proteins, cruciferous vegetables, fatty fish, whole eggs, nuts, legumes, whole grains, chili peppers, avocados, cottage cheese, chia seeds, Greek yogurt, sweet potatoes, ginger and turmeric, cucumber, and dark chocolate. They help regulate appetite hormones, reduce inflammation, improve digestion, and provide essential nutrients.
Understanding Fat Loss and Metabolism
Fat loss happens when your body burns more calories than it consumes, creating a calorie deficit. Metabolism also influences how quickly your body converts food into energy. Some foods have a high thermic effect, meaning your body uses more energy to digest them, which supports fat loss. Prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense foods over processed options helps maintain metabolism and supports lasting weight loss.
Criteria for Fat-Cutting Foods
Fat-cutting foods share key characteristics:
- High protein content to increase fullness and preserve muscle
- Low calorie density but high fiber for lasting satiety
- Contain compounds that boost metabolism such as antioxidants, capsaicin, and healthy fats
Diet Plan For Weight Loss; 17 Natural Fat-Cutting Foods

Here are detailed explanations of 17 foods proven to help cut fat naturally, with their nutritional highlights and fat-burning mechanisms.
- Leafy Greens (Kale, Spinach, Collards)
Leafy greens are low in calories and high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They help fill you up without adding many calories. The fiber improves digestion and can enhance fat metabolism, making leafy greens ideal for weight management.
- Lean Proteins (Skinless Poultry, Fish, Lean Beef, Eggs)
Lean proteins increase satiety and muscle preservation. Protein takes more energy to digest, boosting metabolism via the thermic effect. Including sources like chicken breast, turkey, egg whites, and lean cuts of meat helps reduce fat while maintaining muscle.
- Cruciferous Vegetables (Broccoli, Cauliflower, Cabbage)
Cruciferous veggies are fiber-rich and contain antioxidants that reduce inflammation and support fat burning. Their high nutrient density with low calories aids digestion and energy expenditure, all contributing to fat loss.
- Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Sardines)
Fatty fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce inflammation and improve fat metabolism. They also provide high-quality protein that supports muscle on a fat loss diet and help regulate hormones that control appetite.
- Whole Eggs
Whole eggs pack protein and healthy fats, which promote fullness and steady energy. Despite past misconceptions, eggs do not increase fat gain when eaten in moderation and are effective for weight loss due to their nutrient balance.
- Nuts (Almonds, Walnuts)
Nuts contain healthy fats, protein, and fiber, all of which increase satiety. Eating nuts in moderation can improve metabolism and assist fat loss by reducing hunger and controlling blood sugar spikes.
- Legumes (Beans, Lentils, Chickpeas)
Legumes provide both protein and fiber, making them satisfying and metabolism-friendly. Their complex carbs help sustain energy and prevent overeating, aiding healthy fat reduction.
- Whole Grains (Quinoa, Brown Rice, Oats)
Whole grains are rich in fiber and nutrients, providing slow-releasing energy that keeps hunger at bay. Their fiber content supports digestion and fat metabolism better than refined grains.
- Chili Peppers (Capsaicin Benefits)
Chili peppers contain capsaicin, a compound that increases metabolism and fat burning. Capsaicin also reduces appetite, making spicy foods a natural aid in cutting fat.
- Avocados (Healthy Fats and Fiber)
Avocados are a great source of monounsaturated fats and fiber. These healthy fats help regulate hunger hormones while fiber improves fullness, supporting fat loss efforts.
- Cottage Cheese (Protein and Calcium)
Cottage cheese provides a high amount of protein with low calories and calcium, which some studies suggest can help increase fat breakdown. Its slow-digesting casein protein aids muscle maintenance during calorie restriction.
- Chia Seeds (Fiber, Omega-3 Fatty Acids)
Chia seeds expand in the stomach absorbing water, creating fullness. Their fiber content slows digestion and their omega-3s support fat metabolism and reduce inflammation.
- Greek Yogurt (Probiotics, Protein)
Greek yogurt is high in protein and contains probiotics which support gut health. A healthy gut microbiome can improve weight management and fat loss by optimizing digestion and inflammation control.
- Sweet Potatoes (Fiber and Antioxidants)
Sweet potatoes provide fiber and antioxidants which promote a balanced response to insulin and regulate blood sugar. Their high fiber content supports fullness and fat metabolism.
- Ginger and Turmeric (Anti-Inflammatory, Metabolic Benefits)
These spices reduce inflammation and encourage fat burning by enhancing metabolism. Regular intake may aid digestion and support weight loss efforts naturally.
- Cucumber (High Water Content and Antioxidants)
Cucumbers are low-calorie and mostly water with antioxidants that help eliminate toxins. They are hydrating and filling, aiding overall digestion and healthy weight loss.
- Dark Chocolate (Antioxidants, Satiety Support)
Dark chocolate, especially varieties with 70% or more cocoa, contains antioxidants that improve metabolism and enhance feelings of satisfaction, reducing cravings for unhealthy sweets.
Lifestyle Factors That Complement a Fat-Cutting Diet
Successful fat loss is not only about including fat-cutting foods in your diet but also adopting supportive lifestyle habits that enhance your body’s ability to burn fat and maintain overall health. Here are key lifestyle factors to incorporate alongside your fat-cutting diet.
- Regular Physical Activity
Engage in consistent exercise combining both cardio and strength training. Cardio boosts calorie burn and enhances heart health, while strength training preserves and builds muscle, which increases resting metabolism and helps maintain fat loss over time.
- Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water supports digestion, helps control appetite, and can slightly increase metabolism. Hydration also aids in the efficient breakdown and transport of fats and nutrients throughout the body.
- Prioritize Quality Sleep
Aim for 7 to 9 hours of restful sleep each night. Poor sleep disrupts hunger-regulating hormones like ghrelin and leptin, often increasing cravings and reducing the body’s ability to control weight effectively.
- Manage Stress
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can promote fat storage, especially around the abdomen. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or spending time in nature to support hormonal balance.
- Limit Processed and Sugary Foods
Minimize intake of highly processed, sugary, and refined carbohydrate-rich foods that spike blood sugar and insulin levels. These can hinder fat loss by promoting fat storage and increasing hunger.
- Consistent Meal Timing
Adopt a regular eating schedule to help regulate metabolism and hunger signals. Avoid skipping meals to prevent overeating later and support steady energy levels.
Common Myths About Fat-Cutting Foods
Common myths about fat-cutting foods often mislead people into unrealistic expectations or ineffective habits. Here are some key myths debunked:
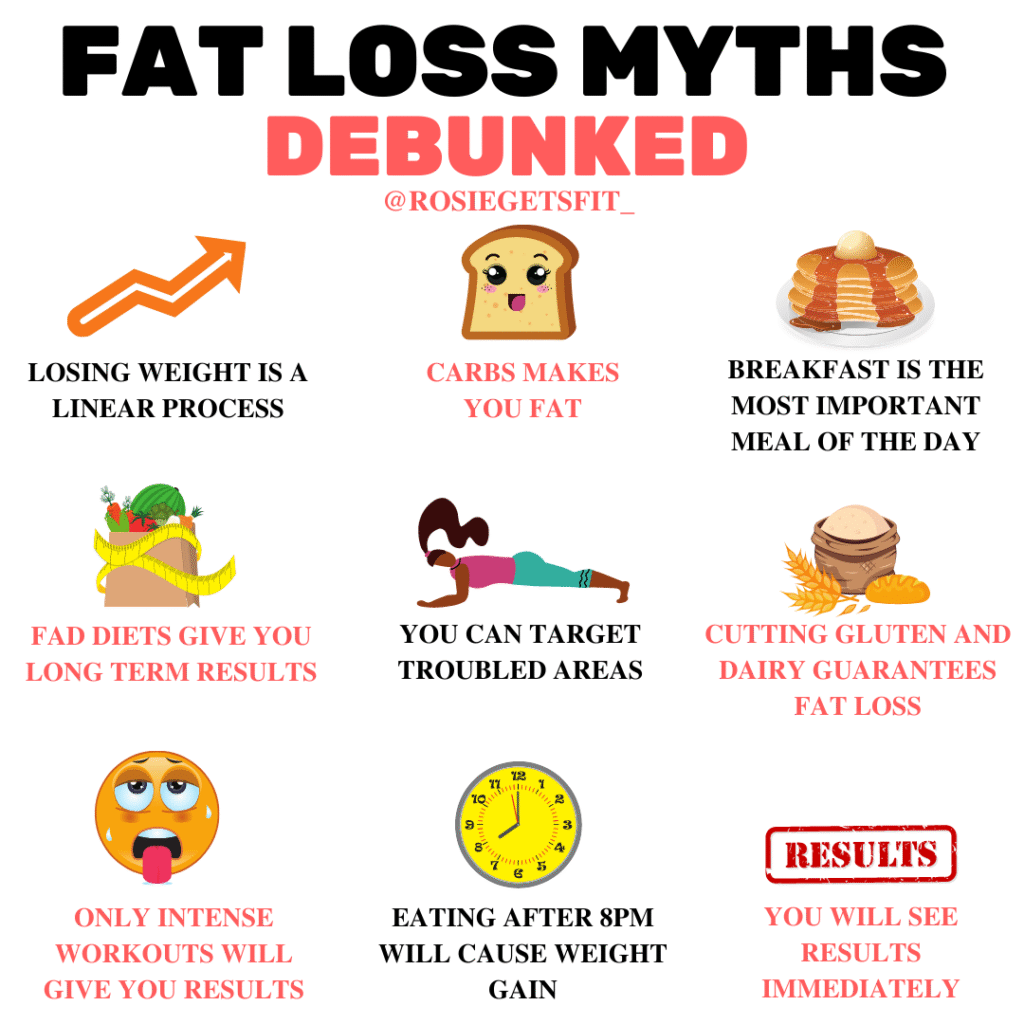
Myth 1: Fat-Cutting Foods Alone Will Cause Weight Loss
No single food or group of foods can magically burn fat on its own. Fat loss depends on creating a calorie deficit through a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle. Fat-cutting foods support this process by boosting metabolism, increasing fullness, and improving nutrition, but they are not standalone solutions.
Myth 2: Eating More Fat-Cutting Foods Means You Can Eat Unlimited Calories
Even healthy, fat-cutting foods contain calories. Overeating any food, regardless of its metabolism-boosting properties, can prevent weight loss. Portion control remains essential for maintaining a calorie deficit.
Myth 3: All “Fat-Burning” Foods Are Spicy or Exotic
While some spices like chili peppers do contain metabolism-enhancing compounds, many common foods like leafy greens, eggs, and nuts also support fat loss. Fat-cutting foods come from a wide range of familiar, everyday ingredients.
Myth 4: You Can Target Fat Loss on Specific Body Areas by Eating Certain Foods
Spot reduction, or losing fat from a specific body part by eating certain foods, is a myth. Fat loss happens systemically across the body depending on overall calorie balance, genetics, and activity levels.
Myth 5: Supplements Are More Effective Than Whole Foods for Fat Loss
Whole foods provide a broad range of nutrients, fiber, and beneficial compounds that supplements can’t fully replicate. Fat-cutting effects are best achieved through a balanced diet rich in natural foods rather than relying on pills or powders.
Myth 6: Fat-Cutting Foods Work Without Exercise
Exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle, boosting metabolism, and increasing calorie burn. Combining fat-cutting foods with regular physical activity produces the best results.
Myth 7: Fat-Cutting Foods Work Immediately
Fat loss is a gradual process. While fat-cutting foods improve metabolic health and support a calorie deficit, consistent eating habits over time are necessary to see meaningful, sustained weight loss.
Conclusion
Including natural fat-cutting foods in your diet can support weight loss by boosting metabolism, improving satiety, and enhancing nutrient intake. Foods like leafy greens, lean proteins, fatty fish, nuts, and whole grains work together to preserve muscle, regulate appetite hormones, and reduce inflammation. However, these foods are most effective when combined with healthy lifestyle habits such as regular exercise, good hydration, quality sleep, stress management, and limiting processed foods.
Sustainable fat loss comes from a balanced approach that prioritizes nutrient-rich eating and consistent habits, ensuring you achieve results that last while maintaining overall health and energy.
FAQs
- What makes food fat-burning?
Foods that boost metabolism, increase fullness, or support fat oxidation. - Can eating these 17 foods alone lead to weight loss?
No, they must be part of a calorie-controlled diet with regular exercise. - How often should I eat these foods?
Daily inclusion in balanced meals is ideal for sustained fat loss. - Are there side effects of eating too much of these foods?
Moderation is key; excess fiber or fats can cause digestive issues. - Can these foods help reduce belly fat specifically?
They support overall fat loss, but spot reduction is not possible. - How do chili peppers help fat loss?
Capsaicin increases metabolic rate and suppresses appetite. - Are supplements better than whole fat-cutting foods?
Whole foods provide broader nutrients and are more effective for health. - Can vegetarians get fat-cutting benefits?
Yes, many plant-based options like legumes, nuts, and seeds are effective. - How does protein in these foods help metabolism?
Protein has a high thermic effect and preserves muscle during calorie deficit. - Is exercise necessary for fat-cutting foods to work?
Exercise enhances fat loss results when combined with a good diet.
Reference
- Fat loss and metabolic mechanisms involving diet and calorie deficit:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10918523/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7539343/ - Benefits of leafy greens for weight management through fiber and nutrient density:
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/most-weight-loss-friendly-foods
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/health-fitness/weight-loss/5-leafy-greens-to-include-in-your-weight-loss-diet/photostory/95145461.cms - Lean proteins promoting fullness, muscle preservation, and increased metabolism:
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/how-protein-can-help-you-lose-weight
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7539343/ - Fat-burning effects of cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage):
https://www.webmd.com/diet/health-benefits-cruciferous-vegetables
https://draxe.com/nutrition/cruciferous-vegetables/ - Omega-3 fatty acids in fatty fish supporting fat metabolism and reducing inflammation:
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/11-healthy-foods-that-help-you-burn-fat
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7561009/ - Capsaicin in chili peppers boosting metabolism and appetite control:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5426284/
https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/effects-of-capsaicin-intake-on-weight-loss-among-overweight-and-obese-subjects-a-systematic-review-and-metaanalysis-of-randomised-controlled-trials/AF1C3A4331A35BA12CE925B0B56818B8 - Avocados aiding fullness and fat loss with healthy fats and fiber:
https://avocadosfrommexico.com/health/avocado-good-weight-loss/
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/avocados-and-weight - Chia seeds and Greek yogurt benefits for satiety and gut health:
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/most-weight-loss-friendly-foods
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/how-probiotics-can-help-weight-loss - Dark chocolate’s antioxidants and satiety support:
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/11-healthy-foods-that-help-you-burn-fat - Lifestyle factors supporting fat loss such as exercise, hydration, and sleep:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/weight-loss/art-20044318
Aubrey Carson is an RDN with 9 years across hospital, outpatient, and private practice settings. They earned an MS in Clinical Nutrition from Tufts University – Friedman School (2016) and completed a Dietetic Internship at Mayo Clinic. Aubrey specializes in micronutrient assessment, evidence-based supplementation, and patient education. Their work includes CE presentations for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and collaborations with Mass General Brigham on nutrition education resources.


