
Probiotics have gained significant attention for their role in promoting digestive, immune, and overall health. These “good bacteria” naturally reside in the gut and help maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in the body. Understanding probiotics benefits and side effects is essential for anyone looking to improve their health naturally. Incorporating probiotics through foods or supplements can support digestion, enhance immunity, and contribute to overall wellness, while knowing potential side effects ensures safe and effective use.
Key Takeaways
- Probiotics benefits and side effects are important to understand before starting supplementation.
- Probiotics support digestive health, immune function, and may improve mental well-being.
- They are found naturally in fermented foods or as dietary supplements.
- Mild side effects may occur, especially when first introducing probiotics.
- Choosing the right strains and doses maximizes benefits while minimizing risks.
What Is Probiotics

Probiotics are beneficial bacteria and yeasts that naturally reside in the digestive system. They play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy balance between “good” and “bad” bacteria in the gut. When this balance is disrupted by poor diet, antibiotics, stress, or illness, it can lead to digestive problems, weakened immunity, and other health concerns. Consuming probiotics through foods or supplements helps restore this balance and supports overall gut function.
These beneficial microorganisms do more than just aid digestion. They also enhance immune function, reduce inflammation, and contribute to overall wellness. By incorporating probiotics into your daily routine, either through fermented foods or high-quality supplements, you can improve nutrient absorption, promote a healthy gut environment, and reduce the risk of infections and digestive discomfort.
How Probiotics Work
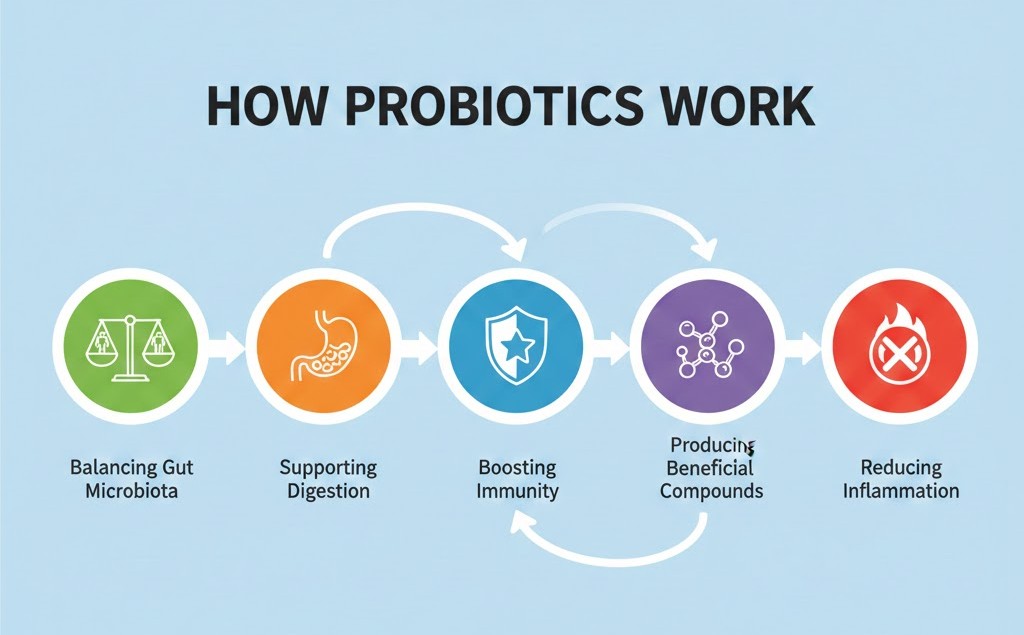
Probiotics support overall health by maintaining a balanced gut microbiota and improving digestive, immune, and metabolic functions. They replenish beneficial bacteria in the gut, preventing harmful bacteria from overgrowing and causing infections or digestive disturbances. This balance is essential for smooth digestion, nutrient absorption, and protection against pathogens.
Key ways probiotics work include:
- Balancing Gut Microbiota: Replenish good bacteria to maintain equilibrium and prevent harmful bacteria from dominating.
- Supporting Digestion: Aid in breaking down complex foods, enhancing nutrient absorption, and reducing bloating, gas, or constipation.
- Boosting Immunity: Strengthen the gut barrier and stimulate immune cells, helping the body fight infections more effectively.
- Producing Beneficial Compounds: Some strains produce vitamins, short-chain fatty acids, and other compounds that support gut health and metabolism.
- Reducing Inflammation: Probiotics can calm gut inflammation, benefiting conditions like IBS and other digestive disorders.
Probiotics Benefits and Side Effects
Probiotics offer numerous health benefits, supporting digestion, immunity, and overall wellness. These beneficial microorganisms help maintain a balanced gut microbiota, which is essential for optimal nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mental well-being. Including probiotics through foods like yogurt, kefir, or fermented vegetables or via supplements can improve digestive comfort, reduce infection risk, and promote long-term gut health.
Key Benefits of Probiotics
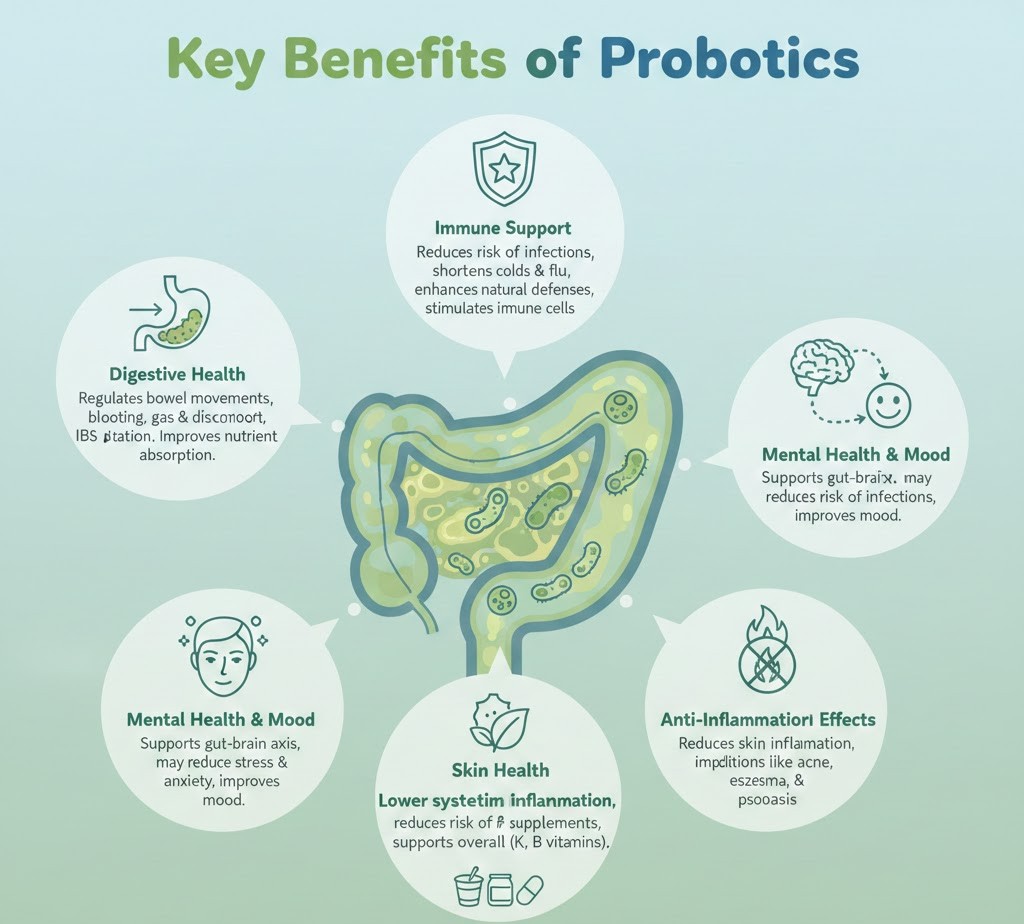
Incorporating probiotics into your diet supports gut balance, digestion, immunity, mental well-being, and overall health. Regular intake through foods or supplements can reduce digestive discomfort, lower inflammation, and strengthen your body’s defenses.
- Digestive Health: Probiotics help regulate bowel movements, reduce bloating, gas, and discomfort, and may relieve symptoms of IBS, diarrhea, or constipation. By restoring a healthy balance of gut bacteria, they improve nutrient absorption and support overall digestive efficiency.
- Immune Support: A balanced gut microbiome is closely linked to immune system strength. Probiotics help reduce the risk of infections, shorten the duration of common colds and flu, and enhance the body’s natural defenses by stimulating immune cells and supporting gut barrier function.
- Mental Health & Mood: Emerging research shows that gut health influences brain function via the gut-brain axis. Probiotics may help manage stress, reduce symptoms of anxiety or depression, improve mood, and support cognitive function through this connection.
- Urinary and Vaginal Health: Certain probiotic strains promote the natural balance of bacteria in the urinary and vaginal tracts, lowering the risk of UTIs and other infections. They help maintain healthy microbiota, which is especially beneficial for women prone to recurrent infections.
- Skin Health: Probiotics may contribute to healthier skin by reducing inflammation associated with acne, eczema, or other skin conditions. A balanced gut microbiome can influence skin hydration, barrier function, and overall appearance.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: By reducing systemic inflammation, probiotics help alleviate conditions linked to chronic inflammation, such as digestive disorders, metabolic issues, and even minor skin irritations.
- Support for Nutrient Synthesis: Some probiotic strains produce essential vitamins, such as B vitamins and vitamin K, and help break down compounds for better nutrient absorption, supporting overall metabolic health.
Possible Probiotic Side Effects
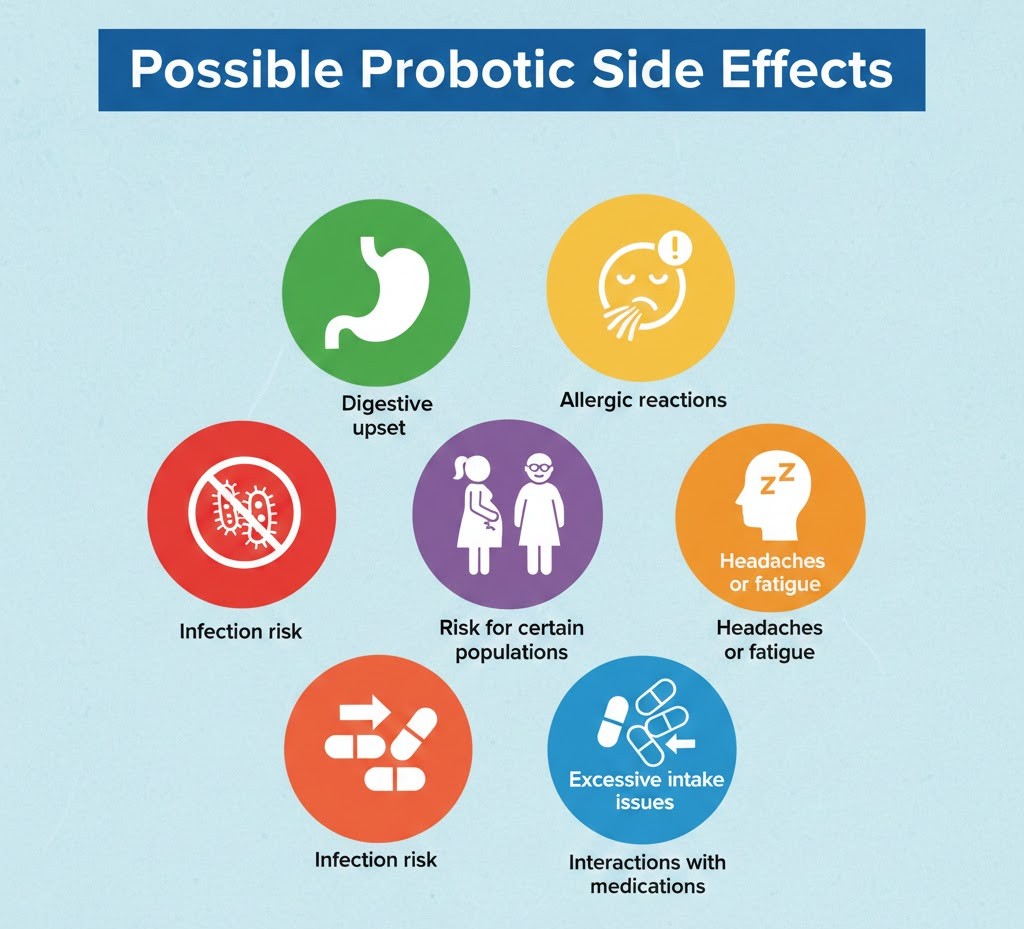
While many individuals experience positive effects from consuming probiotics, it’s important to acknowledge that there can be side effects for some people. Common probiotic side effects include:
- Digestive upset: Initially introducing probiotics to the system can sometimes cause symptoms like gas, bloating, mild stomach discomfort, or loose stools. These symptoms usually subside as the body adjusts.
- Allergic reactions: In rare cases, individuals with allergies to certain strains of bacteria in probiotics might experience allergic reactions such as rashes, itching, or swelling. It’s important to read labels carefully and consult a healthcare professional if you have known allergies.
- Infection risk: People with weakened immune systems, chronic illnesses, or those taking immunosuppressive medications may be at risk of developing infections due to the introduction of live microorganisms through probiotics. Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended.
- Risk for certain populations: Premature infants, critically ill patients, or those with severe underlying health conditions may be more vulnerable to adverse effects from probiotics and should only take them under strict medical supervision.
- Headaches or fatigue: Some individuals report mild headaches or fatigue when first starting probiotics, often due to detoxification or changes in gut microbiota.
- Interactions with medications: Probiotics can sometimes interact with antibiotics or other medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or causing mild complications.
- Excessive intake issues: Taking very high doses of probiotics beyond recommended levels may lead to more pronounced digestive issues or imbalances in gut microbiota.
Ways to Minimize Probiotic Side Effects

While probiotics offer numerous health benefits, some people may experience mild side effects like bloating, gas, or digestive discomfort when starting them. Fortunately, there are practical strategies to reduce these effects and make probiotic use more comfortable. By following these steps, you can enjoy the benefits of probiotics while minimizing potential discomfort:
- Start Slowly: Begin with a lower dose and gradually increase it to allow your gut to adjust.
- Choose the Right Strain: Different strains target different health needs; select probiotics suited for your specific goals.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps your digestive system process the new bacteria smoothly.
- Take With Food: Consuming probiotics with meals can reduce digestive upset.
- Monitor Your Body: Track any changes in digestion or discomfort and adjust intake accordingly.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Essential for people with chronic illnesses, weakened immunity, or during pregnancy.
- Avoid Overuse: Stick to recommended dosages; more is not always better.
- Rotate Products Carefully: Gradually switch between supplements to maintain gut balance.
Common Sources of Probiotics

Including probiotic-rich foods in your diet helps restore gut balance, improve digestion, support immunity, and promote overall health. Different sources offer unique benefits depending on their bacterial strains and nutrient content.
- Fermented Dairy: Yogurt and kefir contain live cultures that support digestive health, enhance nutrient absorption, and strengthen the immune system. Regular consumption can help restore gut bacteria after antibiotics and reduce symptoms of bloating or constipation.
- Fermented Vegetables: Sauerkraut, kimchi, and naturally fermented pickles provide beneficial bacteria along with vitamins and antioxidants. These foods support gut microbiota balance, improve digestion, and reduce inflammation, which may also benefit heart and immune health.
- Other Fermented Foods: Miso, tempeh, and kombucha offer diverse probiotic strains and nutrients that support gut health, aid protein digestion, and promote metabolic and immune functions. They also contribute to a healthy gut-brain connection and overall wellness.
- Probiotic Supplements: Capsules, powders, and liquids containing specific strains target particular health needs, such as improving digestive comfort, enhancing immunity, supporting urinary health, or reducing the risk of recurrent infections. Selecting the right strain and dosage ensures maximum benefits.
How to Choose the Right Probiotics
Selecting the right probiotic is essential to maximize benefits and minimize side effects. Not all probiotics are the same, and different strains serve different purposes. Considering factors like strain type, dosage, and quality can help you choose a product that meets your specific health goals.
- Strain Specificity: Different probiotic strains have unique effects. For example, Lactobacillus rhamnosus may support gut health, Bifidobacterium lactis can enhance immunity, and Lactobacillus reuteri may help maintain urinary and vaginal health. Choosing a strain that aligns with your needs ensures targeted benefits.
- Colony-Forming Units (CFUs): CFUs indicate the number of live microorganisms in a probiotic. While higher counts are not always better, the right dosage depends on the strain and intended purpose. Follow recommended levels on the label or consult a healthcare professional.
- Quality & Storage: Select reputable brands that follow good manufacturing practices. Check expiration dates and storage instructions, as probiotics can lose potency if exposed to heat, moisture, or air.
- Delivery Form: Probiotics are available in capsules, powders, liquids, and fermented foods. Choose a form that suits your lifestyle and ensures optimal absorption.
- Specific Health Needs: Consider your individual health conditions, age, or concerns such as digestive issues, immunity, urinary health, or mental wellness. Consulting a healthcare professional can help identify the most suitable probiotic for your goals.
Common Myths About Probiotics
Despite growing awareness of probiotics, several misconceptions persist. Understanding the facts can help you use probiotics effectively and safely.
Myth 1: All probiotics are the same
Fact: Different probiotic strains have unique effects on digestion, immunity, mental health, and urinary or vaginal health. Choosing the right strain is essential for targeted benefits.
Myth 2: More CFUs means better results
Fact: Higher colony-forming units (CFUs) do not automatically provide better outcomes. Effectiveness depends on the strain, dosage, and individual health needs.
Myth 3: Probiotics work instantly
Fact: Probiotics take time to restore gut balance. Consistent use over days or weeks is usually needed to see improvements in digestion, immunity, or mood.
Myth 4: Probiotics replace a healthy diet
Fact: Probiotics support gut health but cannot replace a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole foods, which are essential for a healthy microbiome.
Myth 5: Probiotics are risk-free for everyone
Fact: While generally safe, probiotics may cause side effects in certain populations, including immunocompromised individuals, critically ill patients, or premature infants. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended.
Myth 6: Only supplements provide probiotics
Fact: Probiotics are naturally present in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, and tempeh. Supplements are optional for specific strains or higher doses.
Myth 7: Probiotics permanently colonize the gut
Fact: Most probiotics provide temporary benefits and do not permanently stay in the gut. Regular intake is needed to maintain their positive effects on digestion, immunity, and overall wellness.
Conclusion
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria and yeasts that help maintain a healthy balance in the gut, supporting digestion, immunity, mental well-being, and overall health. They can relieve digestive issues like bloating, gas, constipation, and diarrhea, strengthen immune function, improve mood via the gut-brain connection, and promote urinary, vaginal, and skin health. Probiotics are found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, and tempeh, or as dietary supplements. While generally safe, some people may experience mild side effects like digestive upset, fatigue, or allergic reactions, and certain vulnerable populations should consult a healthcare professional. Choosing the right strains, dosage, and quality ensures maximum benefits. Gradual introduction and consistent use help maintain gut balance and overall wellness.
FAQs
What are probiotics?
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria and yeasts that naturally live in the digestive system and help maintain a healthy balance of gut microorganisms, supporting digestion, immunity, and overall health.
How do probiotics benefit digestion?
They regulate bowel movements, reduce bloating, gas, and discomfort, and may relieve symptoms of IBS, diarrhea, or constipation by restoring a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
Can probiotics improve immunity?
Yes, a balanced gut microbiome strengthens immune function, lowers infection risk, and helps the body fight illnesses like colds and flu more effectively.
Do probiotics affect mental health?
Emerging research shows probiotics may support mood, reduce anxiety or depression, and improve cognitive function via the gut-brain connection.
What are the possible side effects of probiotics?
Some people may experience mild digestive upset, bloating, gas, fatigue, headaches, allergic reactions, or interactions with medications, especially when first starting probiotics.
Who should be cautious with probiotics?
Premature infants, critically ill patients, people with weakened immunity, or those with severe chronic conditions should consult a healthcare professional before taking probiotics.
How can I minimize probiotic side effects?
Start with a low dose, choose the right strain, stay hydrated, take probiotics with meals, monitor your body, avoid overuse, and consult a healthcare professional if necessary.
What foods are rich in probiotics?
Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, tempeh, and kombucha are natural sources of probiotics that support gut health and overall wellness.
How do I choose the right probiotic?
Consider strain specificity, CFU count, quality, storage, delivery form, and your specific health needs. Consulting a healthcare professional can help identify the most suitable probiotic.
Are probiotics safe for everyone?
While generally safe, probiotics may cause side effects in some individuals. Choosing the right strain, dosage, and consistent use ensures benefits while minimizing risks.
References
- Dr Nicha Somlaw. (2023, October 20). Probiotics: Beneficial Live Microorganisms, Food Sources. MedPark Hospital. Retrieved December 14, 2025, from https://www.medparkhospital.com/zh-CN/lifestyles/probiotics
- Khatri, M. (2023, September 13). Probiotics: Risks and Benefits. WebMD. Retrieved December 14, 2025, from https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/probiotics-risks-benefits
- Peter Kwan. (2024, September 5). Probiotics: Their Side Effects and Benefits of Gut Health. Journal of Probiotics & Health. Retrieved December 14, 2025, from https://www.longdom.org/open-access/probiotics-their-side-effects-and-benefits-of-gut-health-110754.html
- Probiotics: Health benefits and potential risks! (2025, February 8). Peptiko.gr. Retrieved December 14, 2025, from https://peptiko.gr/en/probiotics-health-benefits-and-potential-risks/
- Probiotics: What They Are, Benefits & Side Effects. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved December 14, 2025, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/14598-probiotics
Dr. Carlos Mendoza, MD, PhD, is a rheumatologist and clinical researcher with 15 years of experience in musculoskeletal health, joint preservation, and inflammation management. He earned his PhD in Immunology from University of Toronto and completed his medical residency at Mayo Clinic. Dr. Mendoza’s practice bridges traditional rheumatology with emerging nutraceutical and anti-inflammatory interventions. He has published extensively on cartilage repair and omega-3 supplementation for joint function.

