Maintaining a healthy urinary tract is essential for bladder comfort, kidney function, and overall wellness. Many people turn to urinary tract health supplements to prevent infections, support bladder function, and maintain long-term urinary wellness. While these supplements can provide benefits, it’s important to understand the urinary tract health supplements side effects to use them safely and effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Urinary health supplement risks include digestive issues, allergic reactions, and potential interactions with medications.
- Side effects of UTI supplements vary depending on the ingredients, dosage, and individual sensitivity.
- Bladder health supplements safety is improved when using standardized, high-quality products.
- Negative effects of urinary wellness pills can occur with overuse or improper combination of supplements.
- Understanding the urinary supplements pros and cons helps users make informed choices.
What Are Urinary Tract Health Supplements?
Urinary tract health supplements are specialized products designed to support the normal function of the bladder and urinary system, reduce the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs), and promote overall urinary wellness. These supplements work by supporting the natural defenses of the urinary tract, maintaining a healthy microbial balance, and reducing inflammation or oxidative stress in the bladder and kidneys.
Common types of urinary supplements include:
- Cranberry Extract: Rich in proanthocyanidins (PACs), cranberry extract helps prevent harmful bacteria, especially E. coli, from adhering to the urinary tract lining, lowering the risk of infections.
- D-mannose: This natural sugar binds to bacteria, assisting the body in flushing them out during urination, which may reduce the frequency of recurrent UTIs.
- Probiotics: Certain probiotic strains promote a healthy balance of gut and urinary tract microbiota, which can help prevent bacterial overgrowth and support immune function.
- Herbal and Vitamin Blends: These may include vitamin C, E, or other antioxidants to reduce inflammation, protect urinary tract cells, and enhance overall urinary health.
Natural vs Synthetic Urinary Tract Supplements
Urinary tract supplements are available in both natural and synthetic forms. Understanding the differences between these types can help you choose the most suitable option based on your health needs, preferences, and safety considerations.
| Feature | Natural Supplements | Synthetic Supplements |
| Source | Whole foods, herbs, plant extracts (e.g., cranberry, D-mannose, probiotics) | Lab-manufactured, isolated active ingredients (e.g., vitamin C tablets, standardized PACs) |
| Additional Nutrients | May contain antioxidants, phytonutrients, and other beneficial compounds | Usually only the active ingredient, limited additional nutrients |
| Potency | Can vary depending on source and processing | Standardized and consistent potency |
| Additives | Fewer artificial additives | May contain fillers, binders, or artificial colors |
| Tolerance | Generally well-tolerated but may cause allergies in sensitive individuals | Generally safe but occasional digestive discomfort or allergic reactions |
| Convenience | May require higher doses or larger servings | Easy to dose accurately and convenient for daily use |
| Best For | Those preferring natural, holistic benefits | Those needing precise, reliable dosing and standardization |
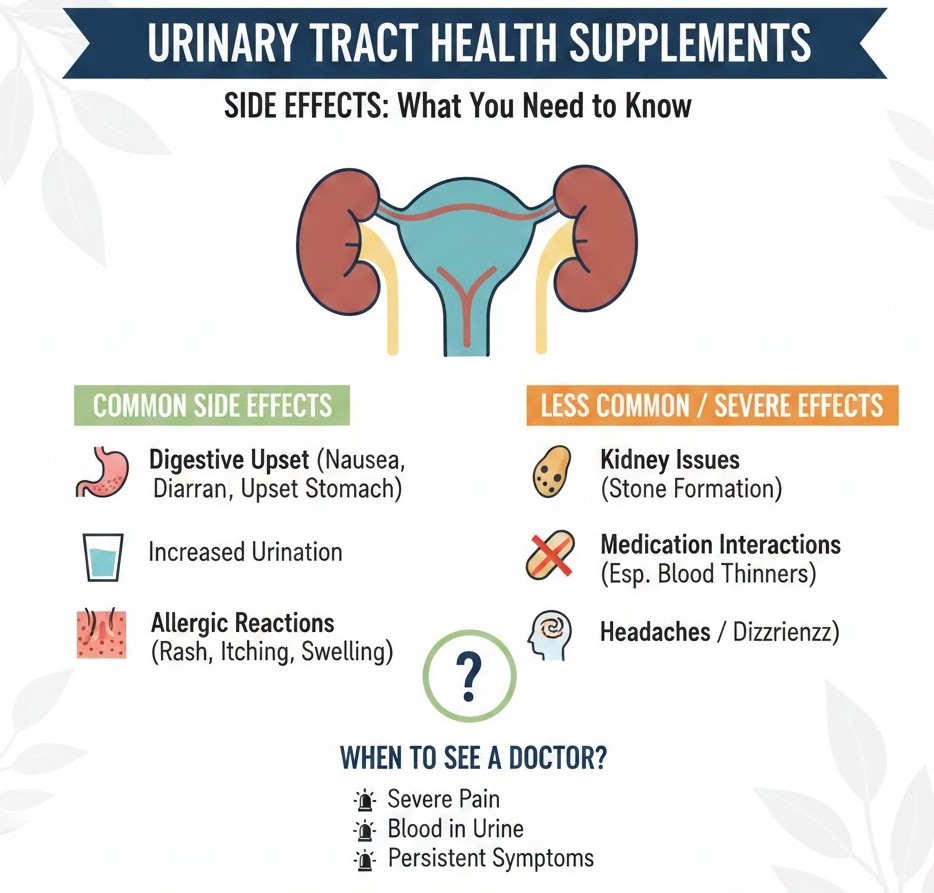
Common Urinary Tract Health Supplements Side Effects
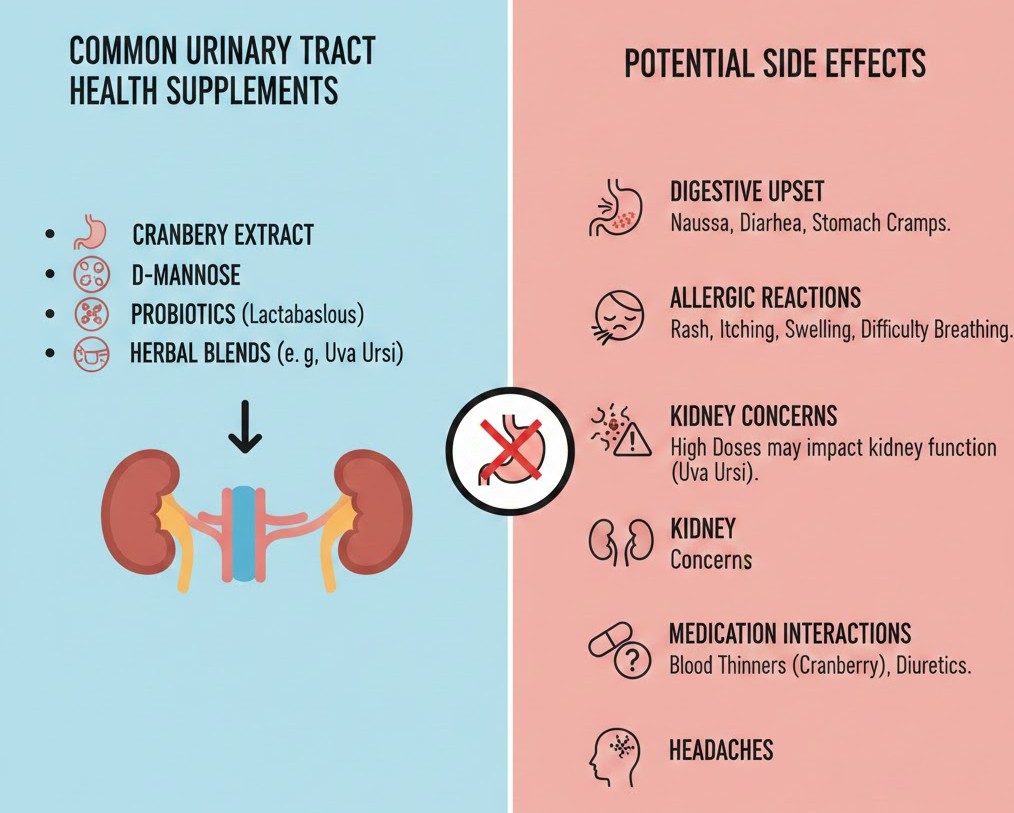
Urinary tract health supplements, including cranberry extract, D-mannose, probiotics, and vitamin C, are generally safe for most people. However, some users may experience mild to moderate side effects depending on dosage, duration of use, and individual sensitivity.
Digestive Issues
Supplements such as cranberry, D-mannose, and probiotics can sometimes irritate the digestive system, causing nausea, bloating, diarrhea, or stomach cramps, particularly when taken on an empty stomach. Taking these supplements with meals and drinking plenty of water can help minimize discomfort.
Allergic Reactions
Some users may experience allergic reactions, including rash, itching, swelling, or, in rare cases, difficulty breathing. These reactions may occur due to herbal components or additional ingredients in the supplements. It is important to check labels carefully and discontinue use if any symptoms appear.
Kidney Stones (Rare)
High doses of vitamin C or concentrated cranberry supplements may increase oxalate levels, potentially contributing to kidney stone formation in susceptible individuals. Symptoms can include pain in the side or back, blood in the urine, or frequent urination. People with a history of kidney stones should consult a healthcare provider before taking high doses.
Blood Thinning Interactions
Cranberry supplements may interact with blood-thinning medications such as warfarin, which can lead to increased bruising or bleeding. Anyone taking blood thinners should inform their doctor before starting cranberry or similar supplements.
Blood Sugar Changes (for Diabetics)
Some cranberry and D-mannose products contain natural sugars that may cause slight fluctuations in blood glucose levels. Individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar closely and consult a healthcare provider when using these supplements.
Probiotic Risks
Probiotics are generally safe but may temporarily cause gas, bloating, or mild digestive discomfort. In rare cases, immunocompromised individuals may be at risk of infections from certain probiotic strains. Starting with a lower dose and consulting a doctor if immune concerns exist can help reduce risks.
Long-Term Use Concerns
Continuous use of urinary supplements without medical guidance may lead to cumulative side effects or mask underlying health issues over time. Following the recommended dosage and checking in periodically with a healthcare provider is advised.
Urine Color or Odor Changes
Natural compounds in cranberry or vitamin supplements can temporarily change the color or odor of urine. These changes are generally harmless and typically resolve once supplementation is paused or stopped.
Long-Term Use Effects of Urinary Supplements
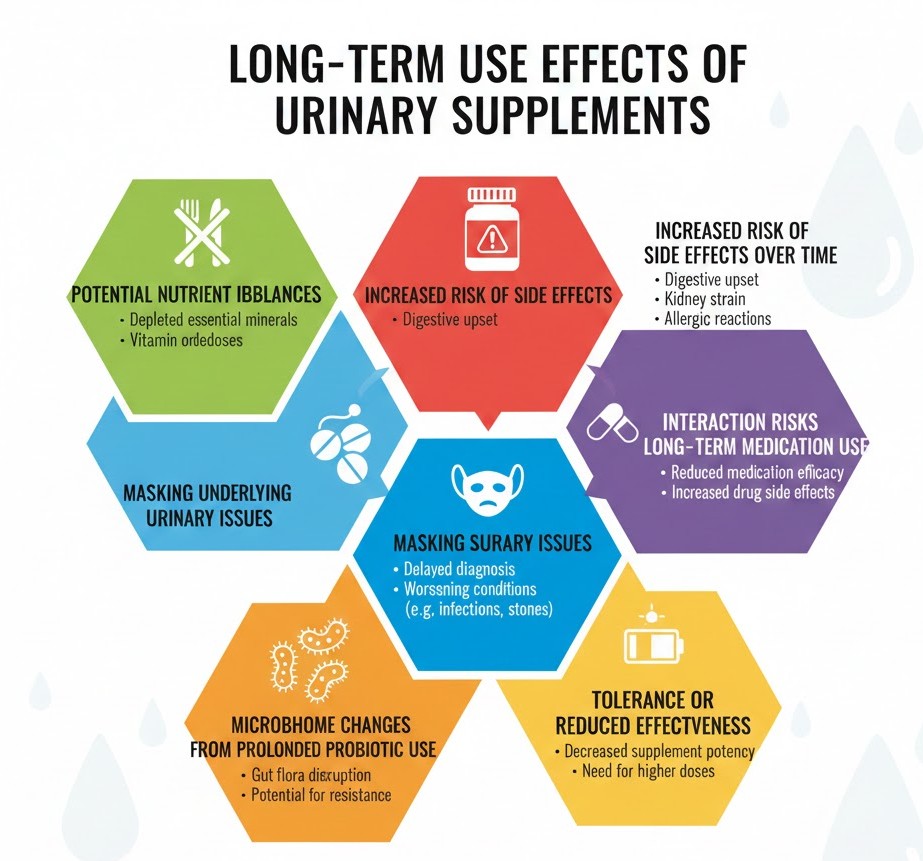
Using urinary tract health supplements over an extended period can offer ongoing support for bladder comfort and UTI prevention, but long-term use also comes with certain considerations. Understanding these effects helps users decide how to use supplements safely and responsibly.
- Potential Nutrient Imbalances: High doses of vitamin C or antioxidant blends over time may raise oxalate levels, slightly increasing kidney stone risk in sensitive individuals.
- Increased Risk of Side Effects Over Time: Long-term use of cranberry, D-mannose, or probiotics may gradually lead to bloating, mild nausea, or digestive discomfort, especially in sensitive users.
- Masking Underlying Urinary Issues: Extended supplement use may hide serious conditions like chronic UTIs or bladder inflammation. Persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a doctor.
- Interaction Risks with Long-Term Medication Use: Daily long-term use may increase interactions with medications such as blood thinners, diabetes drugs, or immune treatments, requiring medical review.
- Microbiome Changes From Prolonged Probiotic Use: Continuous probiotic use may alter gut flora or cause mild gas and discomfort. Taking breaks or rotating strains can help maintain balance.
- Tolerance or Reduced Effectiveness: Some supplements may seem less effective over time due to body adaptation or because an underlying issue needs professional treatment.
- Financial and Practical Considerations: Using multiple supplements long-term can become costly, so reviewing effectiveness regularly helps avoid unnecessary use.
Who Should Avoid Urinary Tract Supplements
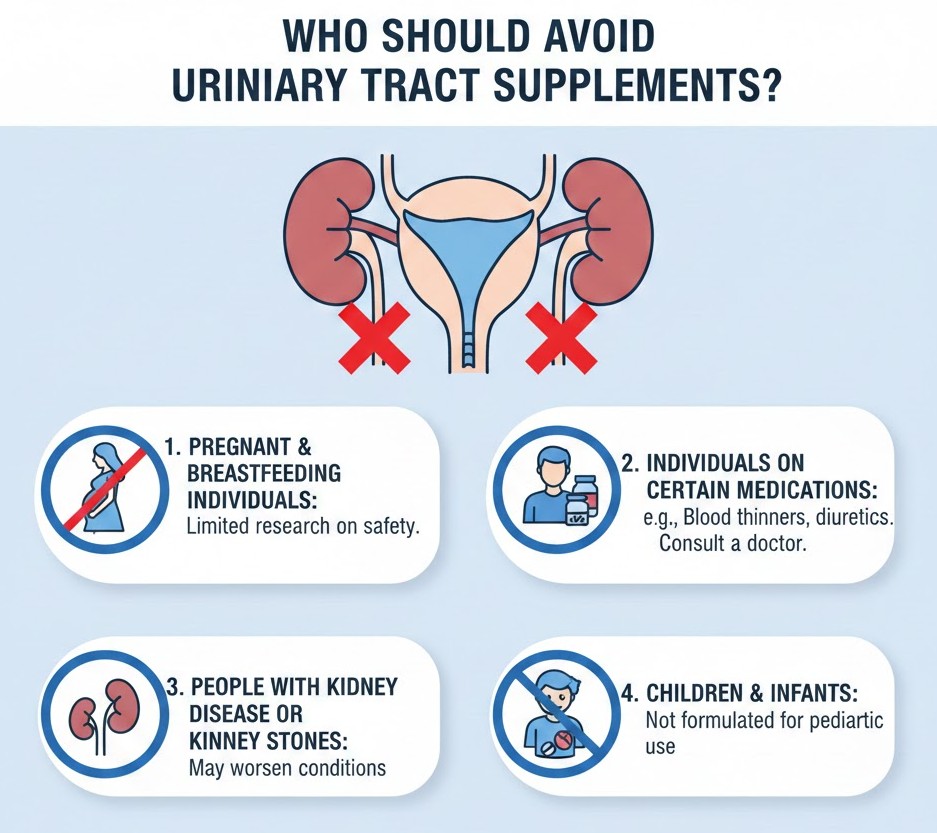
While urinary tract supplements are generally safe for most healthy individuals, certain groups should avoid them or use them only under medical supervision. This helps prevent harmful interactions, kidney strain, or adverse reactions.
- People With Kidney Disease: Individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or reduced kidney function should avoid high-dose cranberry, vitamin C, or herbal blends, as these can increase oxalate levels and put additional stress on the kidneys.
- Individuals With a History of Kidney Stones: Cranberry extract and high vitamin C intake can raise oxalate levels, increasing the risk of stone formation in sensitive users.
- People Taking Blood Thinners: Cranberry products may enhance the effect of blood thinners, increasing the risk of bleeding or bruising.
- Diabetics Taking Glucose-Sensitive Medications: Some supplements (especially those with sweetened D-mannose or cranberry blends) can slightly affect blood sugar levels. Diabetics should consult a doctor before use.
- Immuno compromised Individuals: People with weakened immune systems (due to HIV, chemotherapy, or immune-suppressing drugs) should avoid probiotics without medical approval, as rare infections may occur.
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: Although some ingredients are considered safe, there is limited research on high-dose cranberry, D-mannose, or herbal blends during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Medical guidance is essential.
- People With Known Allergies to Berries, Herbs, or Supplement Additives: Those with food allergies, especially to berries or plant extracts, should check ingredient lists carefully to prevent allergic reactions.
When to Stop Taking Supplements Immediately

Although urinary tract supplements are generally safe, certain reactions signal that your body is not tolerating the product well. If any of the following symptoms occur, stop taking the supplement right away and seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
- Severe Stomach or Abdominal Pain
- Signs of an Allergic Reaction
- Blood in the Urine
- High Fever or Chills
- Severe Back or Flank Pain
- Unusual Bruising or Bleeding
- Rapid Changes in Blood Sugar (for Diabetics)
- Persistent Digestive Distress
When to See a Doctor
While urinary tract health supplements are generally safe, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen. Certain signs may indicate a more serious underlying condition or an adverse reaction to supplements. Seeking medical advice ensures proper diagnosis and prevents complications.
You should see a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent urinary symptoms, such as frequent UTIs, burning or pain during urination, blood in the urine, or unusual discharge.
- Severe pain, including abdominal, back, or flank pain that does not subside.
- Allergic reactions or side effects from supplements that do not improve with time, like rash, swelling, or digestive distress.
- Pre-existing conditions, such as kidney disease, diabetes, or use of long-term medications, which may interact with supplements.
- Routine monitoring for ongoing urinary health, especially if using supplements regularly or long-term.
How to Choose Safe Urinary Supplements
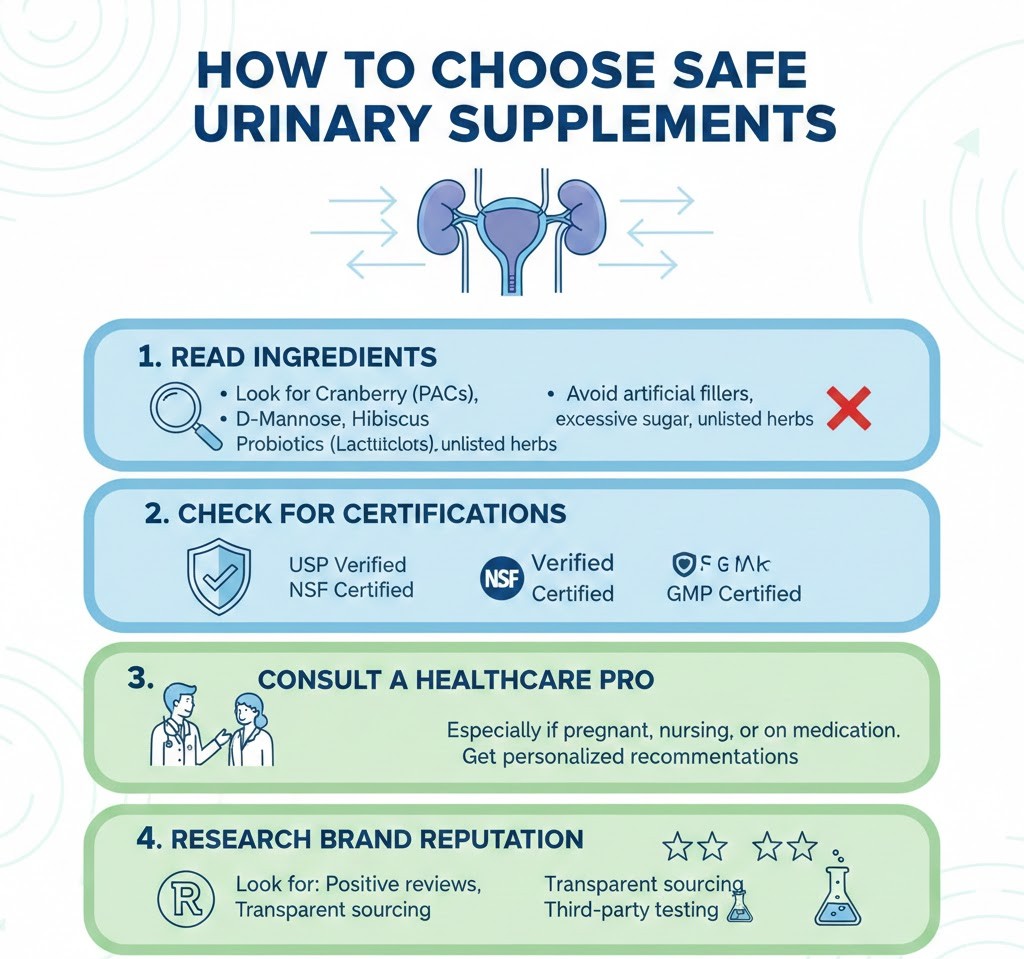
Selecting the right urinary tract health supplements is essential to maximize benefits while minimizing risks. Not all products are created equal, so paying attention to quality, dosage, and formulation can help ensure safety and effectiveness.
1. Look for Standardized Ingredients
Choose supplements that specify the active compounds, such as proanthocyanidins (PACs) in cranberry extract or the exact strains of probiotics. Standardized products ensure consistent potency and effectiveness.
2. Check for Third-Party Testing or FDA Approval
High-quality supplements often undergo independent testing to verify purity, potency, and safety. While dietary supplements are not strictly regulated by the FDA, certifications from third-party labs provide extra assurance.
3. Examine Ingredient Lists Carefully
Avoid products with unnecessary fillers, artificial colors, preservatives, or allergens. Natural and minimal-ingredient formulations reduce the risk of allergic reactions and digestive issues.
4. Choose the Right Form and Dosage
Cranberry, D-mannose, and vitamin supplements come in capsules, tablets, powders, or liquids. Capsules and tablets with standardized doses are often more convenient and reliable for daily use. Follow the recommended dosage instructions to prevent side effects.
5. Consider Your Personal Health Conditions
Consult a healthcare provider before using supplements if you have kidney issues, diabetes, immune disorders, or are taking prescription medications. This helps prevent drug interactions, kidney stress, or other complications.
6. Read Reviews and Brand Reputation
Opt for reputable brands with positive user feedback. Transparent labeling, clear instructions, and responsive customer support are indicators of a trustworthy supplement.
7. Start Slowly and Monitor Effects
When trying a new supplement, start with the lowest effective dose and observe how your body responds. Report any adverse reactions to your healthcare provider promptly.
Lifestyle Tips for Urinary Tract Health

In addition to supplements, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly support urinary tract function and reduce the risk of infections.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Avoid holding urine for long periods, as stagnant urine can encourage bacterial growth.
- Wipe from front to back after using the restroom and maintain proper genital hygiene.
- Choose cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothing to reduce moisture buildup and bacterial growth.
- Eat fruits, vegetables, and probiotic-rich foods to support a healthy urinary and gut microbiome.
- Reduce caffeine, alcohol, and highly acidic or spicy foods that can irritate the bladder.
- Physical activity promotes overall health and supports a healthy urinary system.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy urinary tract is essential for bladder comfort, kidney function, and overall wellness. Many people use supplements like cranberry extract, D-mannose, probiotics, and vitamin blends to support urinary health and prevent infections. Natural supplements provide extra nutrients, while synthetic ones offer consistent potency and easy dosing. Although generally safe, they may cause digestive issues, allergic reactions, kidney stone risk, or interactions with medications, especially in sensitive individuals. Long-term or improper use may mask underlying issues, so consulting a healthcare provider is advised. Alongside supplements, healthy habits like drinking plenty of water, practicing proper hygiene, wearing breathable clothing, eating a balanced diet, and staying active help maintain urinary tract health and reduce infection risk.
FAQs
What are urinary tract health supplements?
They are products like cranberry extract, D-mannose, probiotics, and vitamin blends designed to support bladder function, prevent UTIs, and maintain overall urinary wellness.
Are urinary tract supplements safe for everyone?
Most healthy adults can use them safely, but some may experience digestive issues, allergic reactions, or interactions with medications.
What common side effects should I watch for?
Mild digestive issues (bloating, diarrhea, nausea), allergic reactions (rash, itching), and rarely, kidney stones or blood sugar changes in diabetics.
Can urinary supplements interact with medications?
Yes. For example, cranberry can interact with blood thinners, and some supplements may affect diabetes or immune-related medications.
Are natural supplements better than synthetic ones?
Natural supplements may provide extra nutrients and antioxidants, while synthetic supplements offer standardized doses and more convenient use.
Who should avoid urinary tract supplements?
People with kidney disease, history of kidney stones, those on blood thinners, diabetics, immunocompromised individuals, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and anyone with allergies to ingredients.
Can long-term use of urinary supplements cause problems?
Extended use may mask underlying conditions, increase risk of side effects, alter gut microbiome, or interact with long-term medications.
How can I safely choose urinary tract supplements?
Look for standardized ingredients, third-party testing, minimal fillers, proper dosage, reputable brands, and consult a healthcare provider if you have health conditions.
When should I stop taking a supplement immediately?
Stop if you experience severe abdominal pain, allergic reactions, blood in urine, fever, unusual bruising, or rapid changes in blood sugar.
What lifestyle habits support urinary tract health?
Drink plenty of water, avoid holding urine, practice proper hygiene, wear breathable clothing, eat a balanced diet with probiotics, limit caffeine/alcohol/spicy foods, and stay physically active.
References
- Cranberry Extract Oral: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing. (n.d.). WebMD. Retrieved December 10, 2025, fromhttps://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-18297/cranberry-extract-oral/details#uses
- Erica Julson. (2023, April 18). Are Cranberry Pills Good for You? Benefits, Side Effects and Dosage. Healthline. Retrieved December 10, 2025, fromhttps://www.healthline.com/nutrition/cranberry-pills#side-effects
- Nwadike, V. R. (2024, December 12). D-mannose: Uses, UTIs, benefits, and risks. MedicalNewsToday. Retrieved December 10, 2025, from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323938
- Oliveira, D. (2024, September 25). Cranberry Pills: Health Benefits, How to Take & Side Effects. Tua Saúde. Retrieved December 10, 2025, fromhttps://www.tuasaude.com/en/cranberry-pills/#google_vignette
Eryn Ellison is a PharmD with 8 years in hospital and ambulatory care. A graduate of the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy (2017), Eryn completed a PGY-1 Pharmacy Residency at Cleveland Clinic and holds BCPS certification from the Board of Pharmacy Specialties. They evaluate supplement efficacy, safety, and interactions with common prescriptions. Eryn has authored formulary reviews for P&T committees and consults on deprescribing protocols within large health systems. Credentials: state pharmacist license, BCPS ID, and professional profiles.

